Ingress Protection (IP) ratings indicate how well a device is protected against water or solid particles like dust.
The standard has been set out by the International Electrotechnical Commission, and a device will receive an IP rating code that consists of the letters IP (Ingress Protection), followed by two alphanumeric digits. The higher the number, the better the protection against foreign bodies.
The first numeral rates the enclosure’s protection against solid particles like dust and is rated on a scale from 0 = no protection to 6 = no dust ingress.
The 2nd numeral rates the enclosure’s protection against liquids and is rated on a scale from 0 = no protection to 9 = high-pressure hot water from multiple angles.
Sometimes a number is replaced by an X, which indicates that the device’s enclosure is not yet rated for that specification, therefore ‘IPX6’ for instance, would mean that water projected in powerful jets against the enclosure from any direction would have no harmful effects on the device, while ‘IP6X’ would translate to no ingress of dust; and complete protection against contact (dust-tight). Numerous letters can be used after the IP rating, indicating more protection levels.
Below is a visual guide to understanding what each digit of a device’s enclosure IP rating indicates.
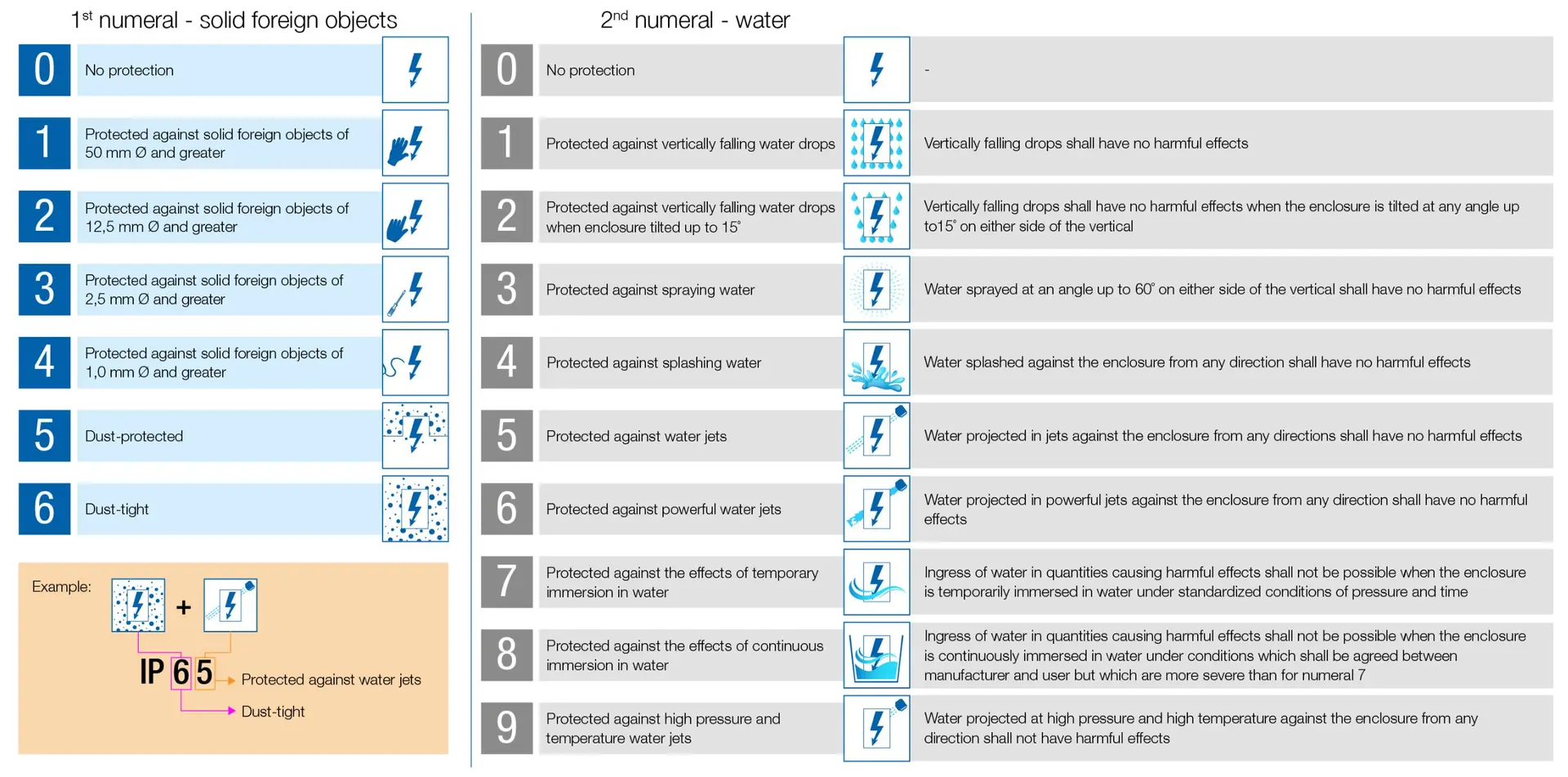
[Source: International Electrotechnical Commission]
There could also be other standards that the device conforms to, such as the MIL-STDs, ATEX & SIL standards, for more specialized applications and environments.
Understanding your operational environment, its technical requirements and IP Ratings can help you choose the best device, with a suitable IP rating to ensure that the device meets its operational requirements and lives up to its full life cycle.